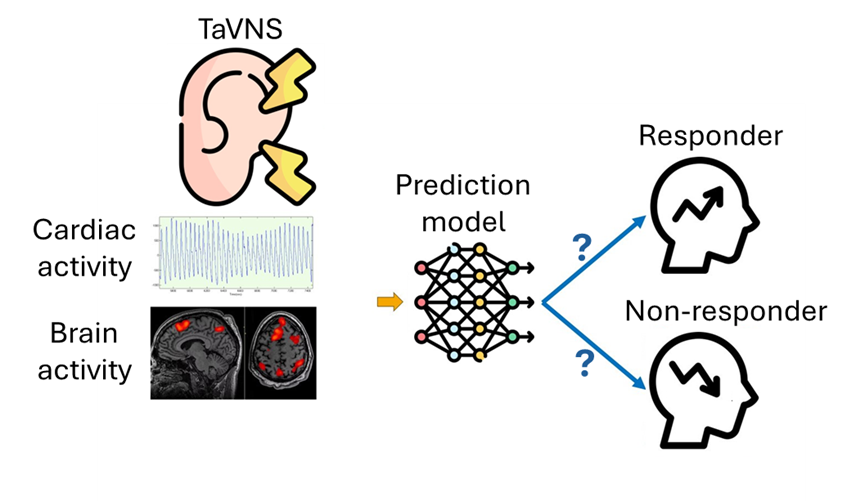
經皮耳迷走神經刺激(taVNS)是一種非侵入性的神經調節技術,已有多項文獻驗證taVNS可治療多類的神經和心理疾病。然而,由於患者對 taVNS 的反應存在差異,識別哪些患者是反應者對於提升臨床治療效果具有重要意義。本研究與廣島大學腦、心與感性科學研究中心合作,共同開發一個高效、準確的預測工具,以在治療前識別出可能受益於 taVNS 的患者,從而提高治療的成功率並降低無效治療的比率。
我們在實驗中收集參與者的大腦結構資料,並量測受試者在接受 taVNS 時 fMRI 和 PPG 資料。針對這些資料進行特徵提取和分析,將可確定與正面治療反應相關的神經和生理指標。
隨後,我們將利用深度學習模型,如卷積神經網路(CNN)或圖神經網路(GNN),對資料進行訓練和驗證,構建一個能夠準確預測反應者的模型。這項研究預期將為 taVNS 的精準化提供重要的工具,促進該技術在臨床中的廣泛應用。
Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (taVNS) is a non-invasive neuromodulation technique that has been shown in multiple studies to be effective in treating various neurological and psychological disorders.
However, responses to taVNS can vary among patients, making it crucial to identify those who are likely to benefit from the treatment to enhance clinical outcomes.
In collaboration with the Center for Brain, Mind, and Kansai Sciences at Hiroshima University, this study aims to develop an efficient and accurate predictive tool to identify patients who may benefit from taVNS before treatment begins.
This approach aims to improve treatment success rates and reduce the incidence of ineffective therapies.
In our experiment, we collected participants' brain structural data using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and measured functional MRI and PPG data during taVNS sessions.
By extracting and analyzing features from these datasets, we seek to identify neural and physiological indicators associated with positive treatment responses.
We will then employ deep learning models, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) or graph neural networks (GNNs), to train and validate a model that can accurately predict responders.
This research is expected to provide a valuable tool for the precision medicine of taVNS, facilitating its broader use in clinical settings.